1.What Is Included In Warehouse Lighting?
A warehouse lighting system refers to the lighting infrastructure installed in a warehouse or distribution center to illuminate the interior space. It is designed to provide adequate and efficient lighting for various activities within the warehouse, such as inventory management, order picking, packaging, and general operations.

A warehouse lighting system typically consists of several components, including:
Lighting Fixtures: These are the physical devices that house the lamps or bulbs. They are designed to distribute light evenly and efficiently throughout the space. Common types of lighting fixtures used in warehouses include high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and fluorescent lights.

Lighting Controls: These are systems or devices used to control and manage the operation of the lighting system. They allow for adjusting light levels, scheduling on/off times, and implementing energy-saving strategies. Examples of lighting controls include occupancy sensors, daylight sensors, timers, and dimmers.
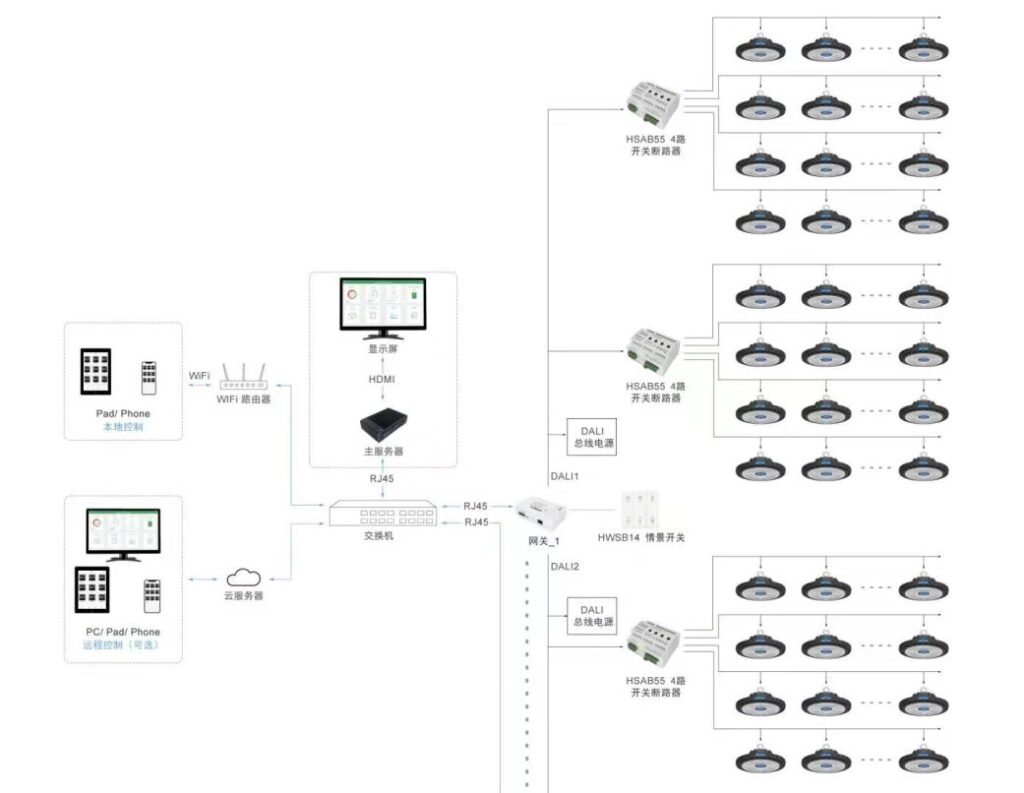
Lighting Layout and Design: The layout and design of the lighting system play a crucial role in ensuring optimal light distribution and minimizing shadows and dark spots. It involves determining the number and placement of lighting fixtures based on the warehouse’s size, ceiling height, and specific requirements.

2.What To Pay Attention When Choose Warehouse Lighting?
When choosing a warehouse lighting system, several factors should be taken into consideration to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here are some key aspects to pay attention to:
2.1 Lighting Requirements: Understand the specific lighting requirements of your warehouse. Consider factors such as the size of the space, ceiling height, type of activities conducted, and any specific lighting standards or regulations that need to be met.
The standard lighting level for a warehouse can vary depending on the specific activities and requirements of the facility. Lux level refers to the measurement of illumination or light intensity in a given area, and it is typically expressed in lux units.
In general, the recommended lux levels for different areas within a warehouse are as follows:
General Storage Areas: Approximately 100-200 lux
These areas are typically used for storing goods that do not require detailed visual inspection or reading small labels or text.

Aisles and Corridors: Around 150-300 lux
Adequate lighting in aisles and corridors is important to ensure safe movement of personnel and equipment and to enable easy identification of products.

Packing and Sorting Areas: About 300-500 lux
These areas require higher lighting levels to facilitate accurate reading of labels, sorting of products, and packaging operations.
Loading Docks: Approximately 150-300 lux
Loading docks need sufficient lighting for safe loading and unloading of goods, as well as inspecting shipments.

Offices and Administrative Areas: Around 300-500 lux
Office spaces within the warehouse should have adequate lighting for general office tasks, such as reading and working on documents.

It’s important to note that these values are general guidelines and may vary depending on specific industry standards, local regulations, and the nature of the warehouse operations. Additionally, certain specialized areas within a warehouse, such as quality control or inspection zones, may require higher lux levels to meet specific visual requirements.
2.2 Energy Efficiency: Look for energy-efficient lighting solutions to minimize electricity consumption and operating costs. LED lighting is known for its energy efficiency and long lifespan. Consider high-efficiency fixtures, such as those with integrated sensors and dimming capabilities, which can optimize energy usage by adjusting light output based on occupancy and daylight levels.
2.3 Lighting Uniformity: Aim for uniform lighting distribution throughout the warehouse to minimize shadows and dark spots. This can be achieved by proper placement and spacing of lighting fixtures. Pay attention to the beam angle and light distribution characteristics of the chosen fixtures to ensure adequate coverage and uniformity.
The recommended lighting uniformity requirements for warehouses can vary depending on the specific activities and industry standards. However, a common guideline followed by many organizations is to achieve a lighting uniformity ratio of at least 0.7 or higher.
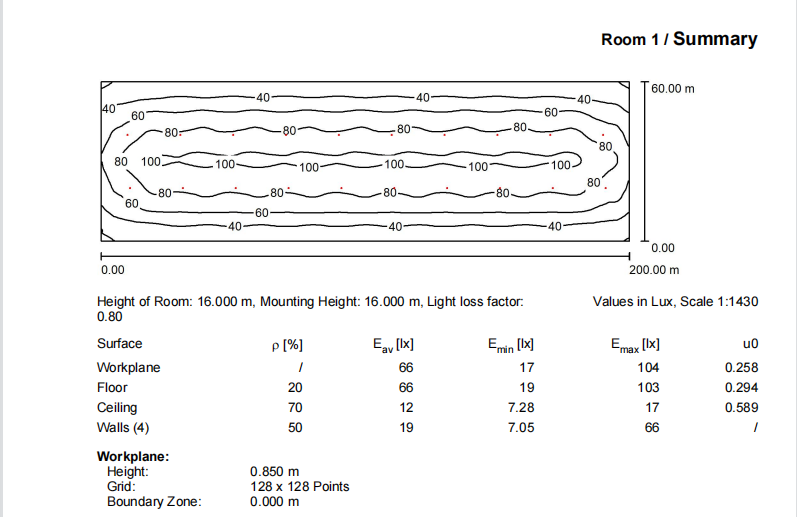
The lighting uniformity ratio is calculated by dividing the minimum illuminance (measured in lux) by the average illuminance in a given area. For example, if the minimum illuminance in a warehouse is 200 lux and the average illuminance is 300 lux, the lighting uniformity ratio would be 0.67, which is below the recommended 0.7.
2.4 Lighting Controls: Implement lighting controls to enhance energy efficiency and provide flexibility in managing the lighting system. Occupancy sensors can automatically turn off or dim lights in unoccupied areas, while daylight sensors can adjust lighting levels based on natural light availability. Timers and scheduling systems can optimize lighting operation based on work shifts and operational hours.

2.5 Maintenance and Lifespan: Consider the maintenance requirements and lifespan of the lighting system. LED lighting generally has a longer lifespan and requires less frequent bulb replacement compared to traditional lighting technologies. Evaluate the ease of maintenance and accessibility of the fixtures to ensure efficient upkeep and minimize disruptions to warehouse operations.
2.6 Safety and Compliance: Ensure that the selected lighting system complies with relevant safety standards and regulations. This includes considerations such as lighting for emergency exits, fire safety, and hazardous material storage areas. Additionally, choose lighting fixtures with appropriate ingress protection (IP) ratings to withstand the warehouse environment’s conditions, such as dust, moisture, or temperature extremes.
2.7 Cost Considerations: Assess the initial cost, installation expenses, and long-term operational costs associated with the lighting system. While it’s essential to consider the upfront investment, also evaluate the potential energy savings, maintenance costs, and lifespan of the lighting system to determine the overall cost-effectiveness.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select a warehouse lighting system that meets your specific needs, provides optimal lighting conditions, promotes energy efficiency, ensures compliance with regulations, and contributes to a safe and productive working environment.
3.Types For Warehouse Lights
There are several types of lighting commonly used in warehouse environments. The choice of lighting type depends on various factors such as the specific requirements of the space, energy efficiency goals, budget considerations, and lighting standards. Here are some of the commonly used types of warehouse lighting:
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lighting: HID lamps, such as metal halide (MH) and high-pressure sodium (HPS), have been traditionally used in warehouses. They provide bright and efficient lighting, making them suitable for high-ceiling spaces. However, HID lamps have longer warm-up times, require ballasts for operation, and have shorter lifespans compared to newer technologies.

Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Lighting: LED lighting has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its energy efficiency, long lifespan, and versatility. LED fixtures provide high-quality, uniform lighting, and can be easily dimmed or controlled. LED lighting is available in various color temperatures, allowing customization based on specific needs. LED lighting is also compatible with advanced controls, enabling further energy savings and flexibility.

Fluorescent Lighting: Fluorescent lights, including T8 and T5 fixtures, have been widely used in warehouses. They offer energy efficiency and good light output, but their popularity has diminished with the rise of LED lighting. Fluorescent lights require ballasts and may not be as durable or long-lasting as LED fixtures.

Induction Lighting: Induction lighting is known for its long lifespan and energy efficiency. It operates by inducing a current in a gas-filled tube using electromagnetic fields. Induction lights provide good color rendering and are often used in areas where frequent maintenance is difficult or costly. However, LED technology has become more prevalent due to its superior efficiency and light quality.

It’s worth noting that LED lighting has become the preferred choice for many warehouse applications due to its energy efficiency, longer lifespan, improved controllability, and overall cost-effectiveness. However, the specific lighting needs and budget constraints of a warehouse should be considered when selecting the appropriate lighting type. Consulting with lighting professionals or suppliers can provide further guidance on the most suitable lighting solution for a particular warehouse setting.
4.What Are The Types For LED Warehouse Lights?
LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology offers various types of lighting fixtures that are suitable for warehouse environments. Here are some common types of LED warehouse lights:
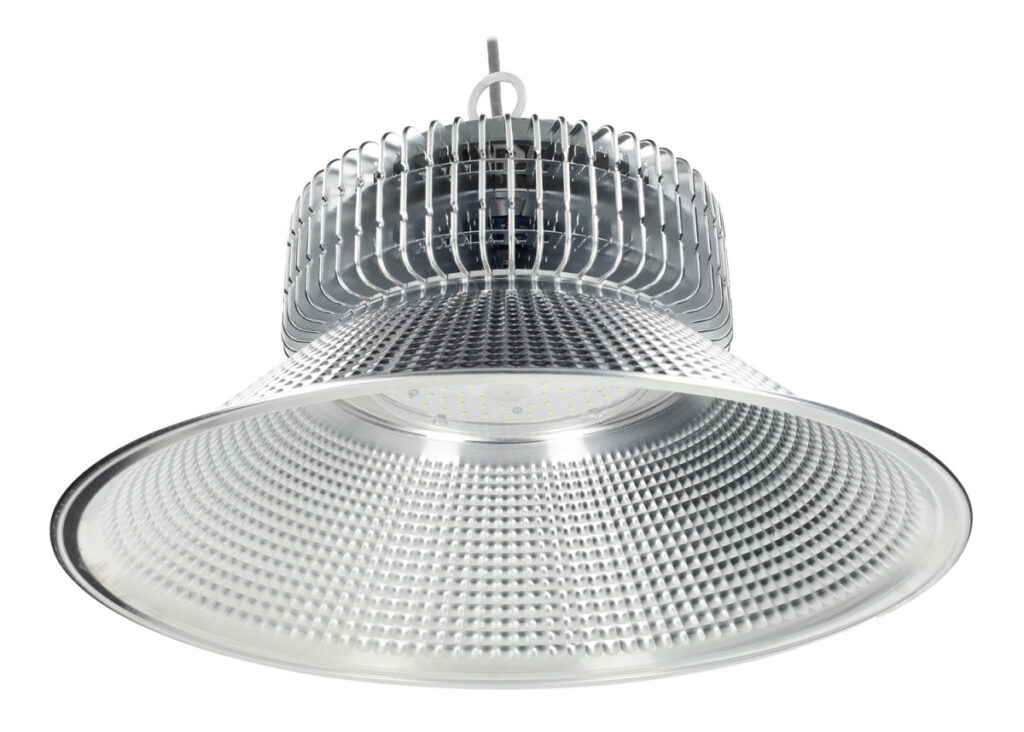
- High Bay Lights: High bay lights are specifically designed for illuminating large, open spaces with high ceilings. They provide powerful, concentrated light that is evenly distributed across the warehouse floor. High bay lights are typically suspended from the ceiling and offer high lumen output and energy efficiency.

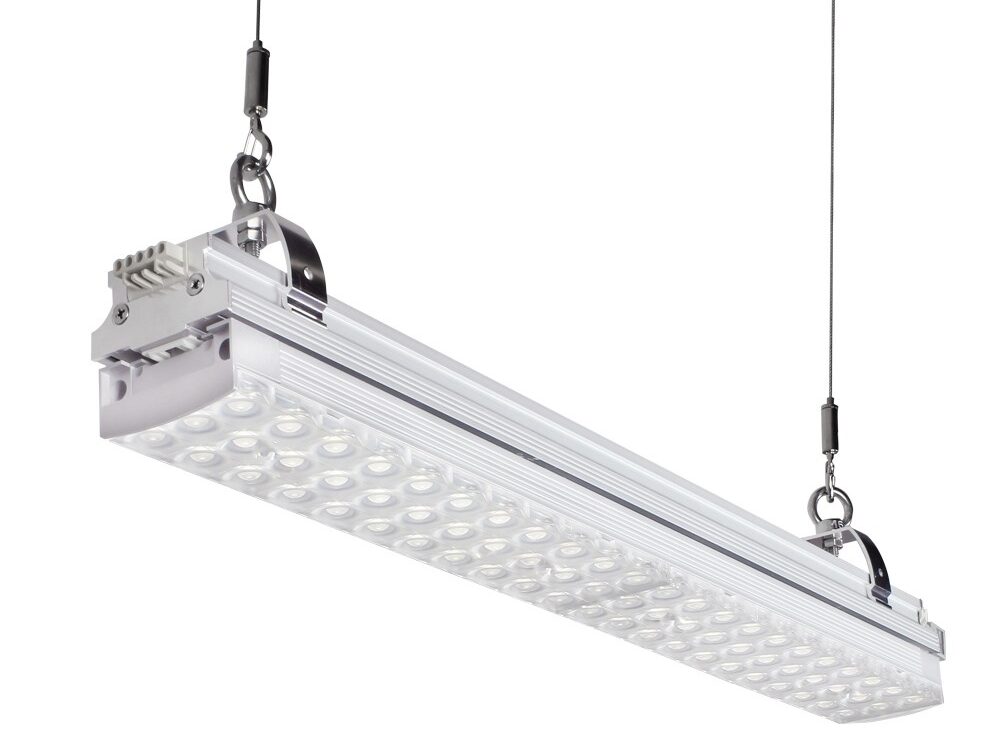
- Linear LED Fixtures: Linear LED fixtures are versatile lighting solutions commonly used in warehouses. They come in different lengths and can be mounted on the ceiling or suspended. Linear LED fixtures provide uniform lighting and are suitable for illuminating aisles, walkways, and storage areas.

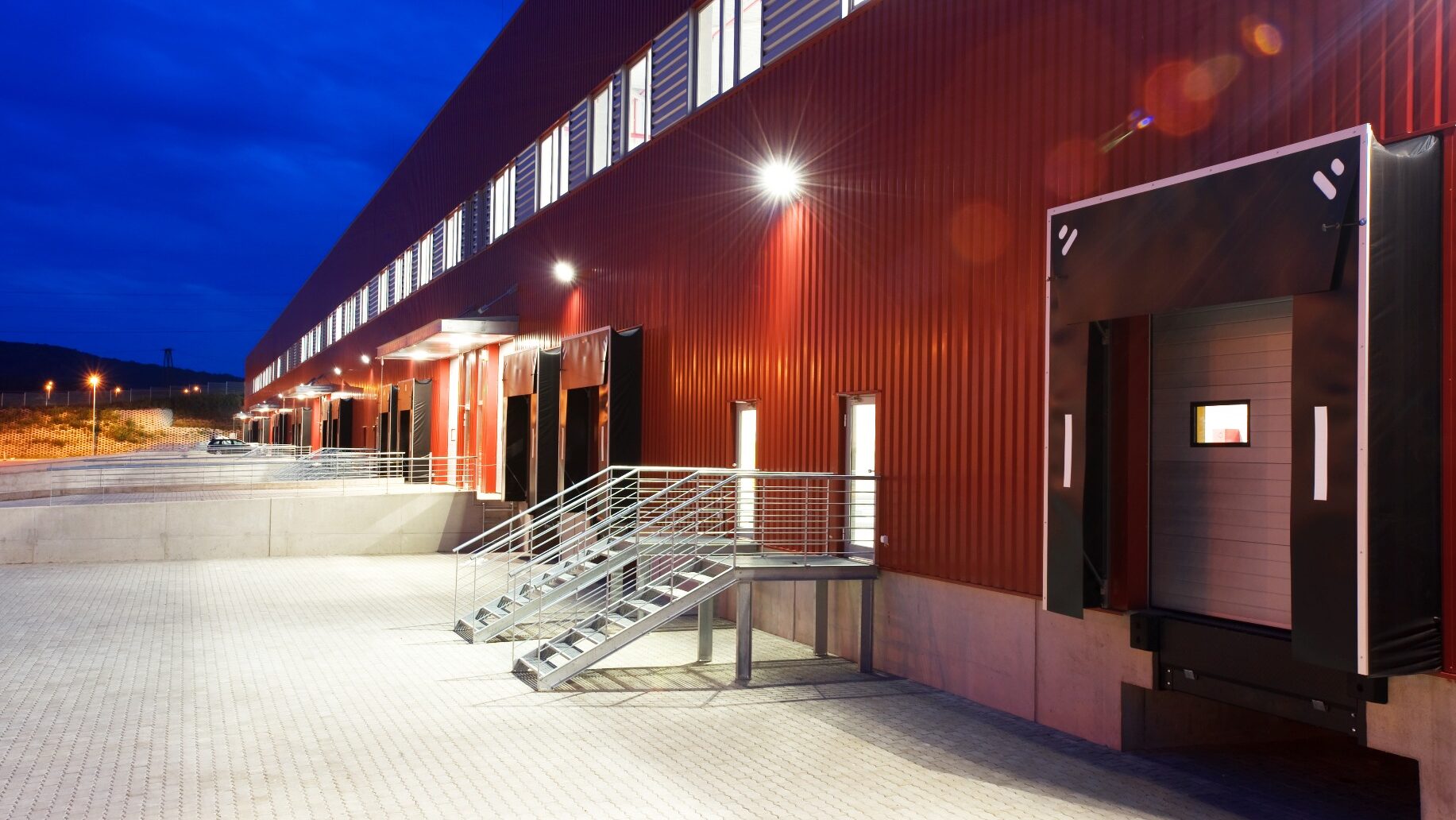
- Floodlights: LED floodlights are used to provide wide-angle illumination over large areas. They are often used in outdoor areas of warehouses, such as loading docks or parking lots. Floodlights offer high lumen output, excellent coverage, and good energy efficiency.

- Wall Pack Lights: Wall pack lights are typically mounted on the walls of warehouses to provide general lighting or security lighting. They are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions and provide a wide, uniform light distribution.

5. Retrofit Kits: LED retrofit kits are designed to replace traditional lighting fixtures, such as metal halide or fluorescent lights, with energy-efficient LED technology. Retrofit kits allow warehouses to upgrade their existing lighting system without the need for a complete fixture replacement.
When selecting LED warehouse lights, consider factors such as the ceiling height, lighting requirements, energy efficiency, and any specific regulations or guidelines applicable to your region or industry. It is advisable to consult with lighting experts or professionals who can provide tailored recommendations based on your warehouse’s specific needs.
5.How To Choose Warehouse Lights?
Choosing the right warehouse lighting involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and compliance with lighting standards. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right warehouse lighting:
Assess The Wattage: Evaluate the lighting requirements of your warehouse by considering the tasks performed in different areas. Determine the desired lighting levels for each zone, such as general storage areas, aisles, order picking areas, and loading docks. Lighting standards, such as those provided by the Illuminating Engineering Society (IES), can serve as a guideline for recommended lighting levels for different types of activities.
Calculate Total Lumen Output: Determine the total lumen output required to achieve the desired lighting levels in your warehouse. Lumen is a unit of measurement that quantifies the total amount of visible light emitted by a light source. Consider the area of each zone and the recommended lighting levels to calculate the total lumen output needed.

Consider Fixture Efficiency: Take into account the fixture efficiency when selecting the wattage for your lighting system. Fixture efficiency is the ratio of the light output of the fixture to the electrical power input. Higher fixture efficiency means more light output per watt of electricity consumed. LED fixtures, for example, are known for their high efficiency compared to traditional HID or fluorescent lighting.
Choose Color Temperature: Consider the color temperature of the lighting to create the desired visual environment. Color temperature is measured in Kelvin (K) and determines the appearance of light. Lower Kelvin values (e.g., 2700K-3500K) produce warm or yellowish light, while higher Kelvin values (e.g., 5000K-6500K) produce cooler or bluish light. The choice of color temperature depends on factors such as the nature of the tasks performed, the desired ambiance, and the color rendering requirements.

Evaluate Lighting Uniformity: Ensure adequate lighting uniformity throughout the warehouse. Lighting uniformity refers to the consistency of light levels across the space. Uneven lighting can create shadows and dark spots, impacting visibility and safety. Proper placement and spacing of fixtures can help achieve better lighting uniformity.
Seek Expert Advice: Consult with lighting professionals or suppliers who specialize in warehouse lighting to get recommendations based on your specific requirements. They can provide insights on the most suitable wattage, fixture type, and other lighting specifications based on their expertise and experience.
It’s important to note that the selection of wattage and other lighting specifications should be based on a careful analysis of your specific warehouse needs. Evaluating lighting standards, consulting with professionals, and considering energy efficiency will help you choose the right wattage and other data to ensure effective and efficient warehouse lighting.
6.Installation Of Warehouse Lighting
The installation of warehouse lighting typically involves several steps and should be carried out by qualified professionals. Here is an overview of the general process:
Planning and Design: Before installation, proper planning and design are essential. This includes determining the layout of lighting fixtures, calculating the number of fixtures needed, and considering factors such as lighting levels, uniformity, and energy efficiency. The lighting design should align with the specific requirements and activities of the warehouse.

Electrical Assessment: Conduct an electrical assessment of the warehouse to ensure that the existing electrical infrastructure can support the lighting system. This may involve evaluating the capacity of the electrical panel, circuitry, wiring, and voltage requirements. If necessary, upgrades or modifications to the electrical system may be required.

Fixture Placement and Mounting: Based on the lighting design plan, determine the optimal placement and mounting height for the lighting fixtures. The fixtures should be strategically located to provide uniform lighting coverage and minimize shadows or dark spots. Install mounting brackets or supports securely to ensure stability.
Electrical Wiring: Connect the lighting fixtures to the electrical supply. This involves running electrical wiring from the fixtures to the electrical panel or distribution system. Wiring should be done in compliance with local electrical codes and regulations. It’s important to ensure proper grounding and use appropriate wiring methods for safety and performance.
Fixture Installation: Install the lighting fixtures according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This typically involves attaching the fixtures to the mounting brackets or supports and making the necessary electrical connections. Follow proper installation procedures to ensure the fixtures are securely fastened and aligned correctly.
Testing and Adjustment: After the fixtures are installed, test the lighting system to ensure proper functioning. Check each fixture for proper operation, including light output, color temperature, and any integrated controls. Make any necessary adjustments, such as repositioning fixtures or fine-tuning lighting levels, to achieve the desired lighting distribution and performance.
7.Conclusion
When selecting LED warehouse lights, consider factors such as the ceiling height, lighting requirements, energy efficiency, and any specific regulations or guidelines applicable to your region or industry. It is advisable to consult with lighting experts or professionals who can provide tailored recommendations based on your warehouse’s specific needs.
8.Looking For A Professional Lighting Supplier? Amber Can Help You!
It’s understandable if you have no idea of how to choose proper lighting for your warehouse . Our professionals at Amber Lighting are available for you 24/7.
We have trained staff here to help you find the required warehouse lights and assess your requirements accordingly. Our experts will resolve all your queries about the warehouse lighting. Contact Us Today!
